As Covid-19 continues to highlight the deficiencies of legacy systems around the globe, prompting high demand for cloud migrations, numerous organizations have been faced with a choice between three cloud models:
• Public Cloud
• Private Cloud
• Hybrid Cloud
Depending on the needs of your organization and the scale of your on-premise infrastructure, a particular model may be ill-suited to meeting your business objectives. Indeed, given that cloud deployment models can have varying impacts on infrastructure, data, and security, it is necessary to consider the benefits and drawbacks associated with each model.
Public Cloud
The public cloud model may simply be understood as a cloud service shared among various customers and organizations. The virtual service itself is provided by a third-party provider (for example, AWS), which offers a pool of resources – anything from software applications to development platforms – that may be allocated to users, on a scalable basis, over the Internet.
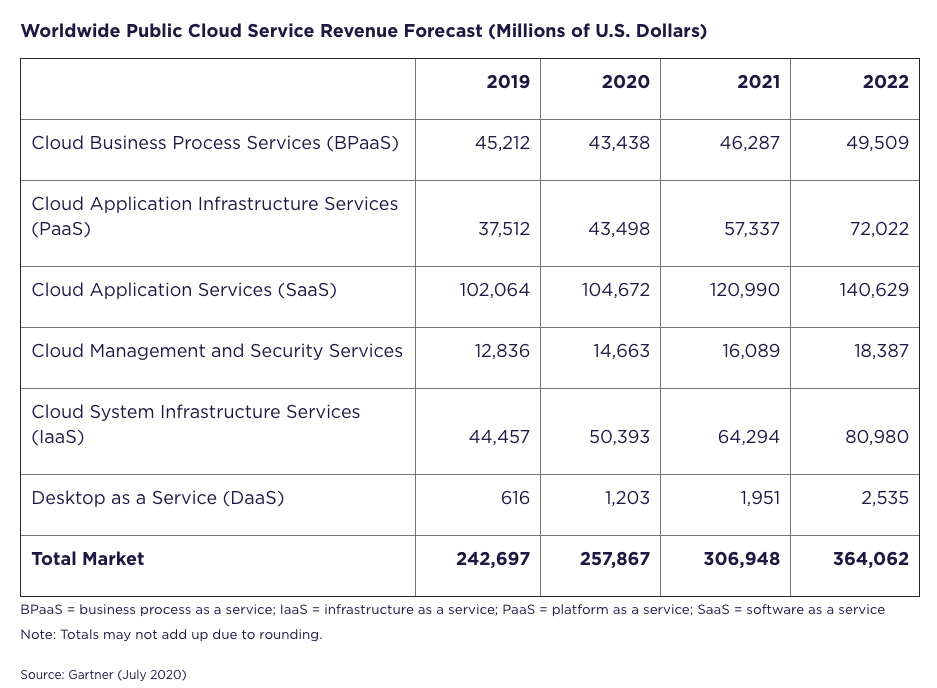
According to Gartner’s forecasts, worldwide public cloud revenues are expected to experience exponential growth, increasing from $257.9 billion (2020) to $364.1 billion in 2022.
Advantages
• Scalable – Public cloud environments offer a great deal of flexibility in terms of being able to provide quick scalability in resources as and when they are needed and in response to unexpected traffic spikes. This is particularly suitable for organizations with fluctuating workloads and demands.
• Cost-Effective – Businesses don’t have to set aside capital for hardware, with the cloud provider covering its provision, maintenance costs and management.
• Reliable – Public cloud vendors virtually ensure reliability of the cloud service, to a greater extent than most businesses are capable of, due to the availability of a broad network of data centers.
Disadvantages
• Security – The multitenant nature of the public cloud may be some cause for concern regarding data security. This is a particular worry for organizations that must comply with a strict level of data security and regulatory compliance.
• Limited Control – Utilizing cloud provider services can be something of a double-edged sword given that you don’t own the necessary hardware (of course, to a certain extent, this is a common issue among cloud deployment models), leaving users with less control and customization flexibility.
• Cost-Anticipation Difficulties – The public cloud’s pay-as-you-go model may lead to some difficulty for organizations in terms of anticipating the full costs of cloud services.
Private Cloud
This cloud model gives an organization exclusive use of a cloud environment, either located in the on-premise data center (internal private cloud) or hosted by the cloud provider itself (hosted private cloud). It should be stressed that the advantages and disadvantages of private cloud use may differ according to the use of an internal or hosted private cloud.
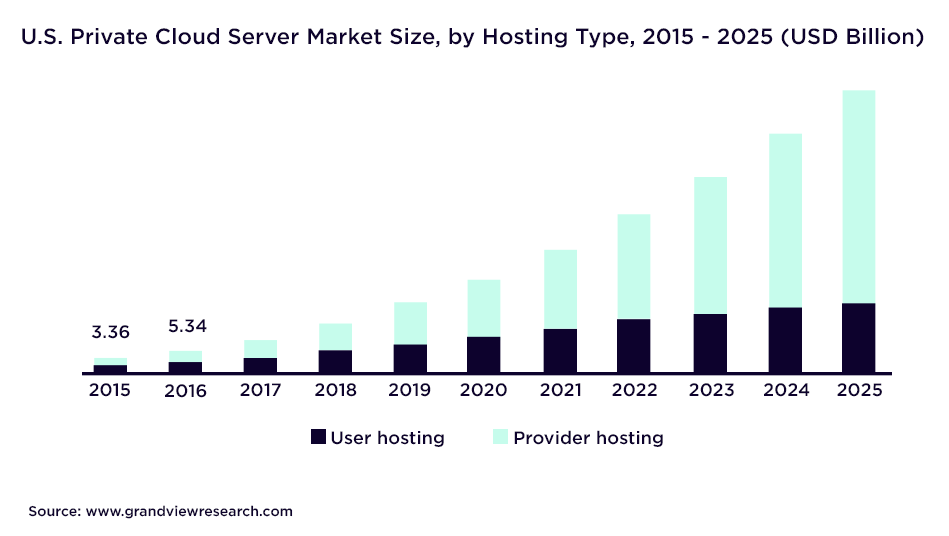
According to Grand View Research’s forecasts, the U.S. private cloud market size is expected to almost quadruple, rising from $60.3 billion (2020) to $205.4 billion by 2025.
Advantages
• Security – As previously mentioned, private cloud environments are more ideal for organizations that handle sensitive data and comply with stricter security and compliance standards often associated with, for instance, FinTech and MedTech industries.
• Flexible Configuration – The use of a private cloud does offer a greater degree of control than what is available to public cloud users. Private cloud environments allow users to benefit from a tailor-made cloud solution, with greater room for customization of cloud configurations, infrastructure, and resources to meet business needs.
• Performance – The exclusivity of resources available to your organization within a private cloud environment can have a positive impact. This is especially important for particular use cases that require greater certainty of high performance, security, and reliability.
Disadvantages
• Added Costs – This particularly relates to the expense involved in arranging an on-premise private cloud environment, with some capital expenditure necessary – in stark comparison to public cloud – for the purchasing and maintenance of hardware (not to mention the need for experienced, in-house IT staff).
• Limited Access – Increased security measures may make accessing the data challenging at times, particularly for mobile users.
• Scalability Issues – The infrastructure available may not offer your organization the same level of scalability as is present within a public cloud environment, particularly if the data center is located on-premise.
Hybrid Cloud
This involves a combination of public and private cloud environments, with the goal of leveraging the benefits of both. Of course, the success of such an approach is contingent on how effectively different environments interact with each other to meet the specific needs of the user.
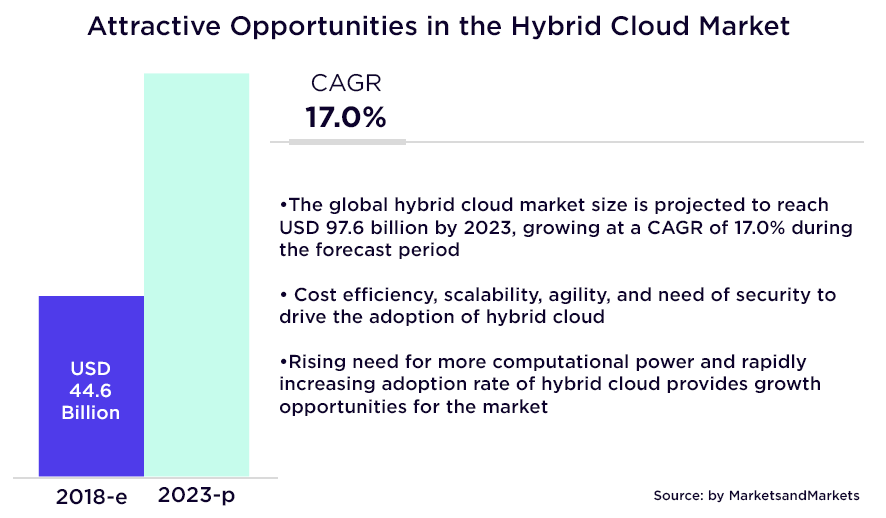
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the hybrid cloud market is predicted to double by 2023, growing from $44.6 billion (2018) to $97.6 billion.
Advantages
• Security-Ensured Scalability – A useful advantage of the hybrid cloud model is that it allows your organization to leverage the scalability of a public cloud environment while securing more sensitive data within a private cloud environment. This is particularly beneficial for those businesses looking to develop applications securely.
•Improved Continuity – A hybrid cloud model’s flexibility of scalability allows organizations to adapt quickly to spikes in traffic, without sacrificing security or overly stressing private servers.
• Reduced Costs – A hybrid cloud environment is a suitable option for businesses that require the advantages of both public and private cloud models (increased security and control of data) in a cost-effective manner.
Disadvantages
• Added Complexity – Depending on the scale of your operations, utilizing a hybrid cloud model may lead to dealing with an unmanageable number of vendors and platforms. Such complexity may require a great deal of IT expertise, to ensure the proper management and maintenance of your cloud operations.
• Visibility Issues – Relating to the aforementioned complexity of a hybrid cloud environment, such a model can complicate an organization’s efforts to maintain a full, comprehensive view over their cloud operations. This can potentially create challenges in terms of a business’ ability to meet regulatory compliance.
• Added Costs – Avoidable expenses may be incurred – without a refined management strategy – if organizations struggle to keep abreast of their cloud infrastructure.
Still unsure about which cloud deployment model is best suited to your organization? Here at VUSE, our cloud migration strategies and solutions are tailored to meet your enterprise’s objectives. Contact VUSE to begin your digital transformation journey today!


