Cloud migration is the process of moving data, applications or other business elements to a cloud computing environment. The main goals for cloud migration are to decrease cost, increase performance, and enhance security.
The three models of cloud migration are: transfer of data and applications from a local data center to a public cloud, moving data and applications from one cloud platform to another called “cloud-to-cloud migration”, and moving data and applications off the cloud to a local data center called “reverse migration”.
Migrating to the cloud allows applications and data to be moved without the added expenses of purchasing more hardware and increase performance and security. Many companies and organizations migrate data and applications from a local data center to a public cloud infrastructure for the benefits of movability, self-service provisioning, redundancy, and a flexible, pay-per-use model.
Cloud Migration Strategies
Moving large amounts of data to the cloud requires a combination of management and technological challenges. While there are choices to how the data will be migrated to the cloud, there are several steps to take and data preferences to consider before initiating the migration process.
Applications
Identify the application. There are plenty of reasons why a company may want to migrate data to a cloud than using local servers. Ensure that the company has the same goals for wanting to converge with a cloud migration. Then, estimate the amount of data that needs to be moved and the estimated time it needs to be completed in. Data and applications will need to be inventoried before the process begins to ensure nothing is lost during the transition.
Every application does not need to leave the company’s data center. The applications that needs to be reviewed are the ones moving from the on-premises units to the cloud. Among those that should stay are applications that are business-critical, have high throughput, require low latency or are applications that have strict geographic stewardship requirements -- such as GDPR -- that may be cause for concern.
Cloud Providers
There are many options to choose from when it comes to cloud service providers. It is important to choose one that is a right fit for the company and for the applications and data being migrated there.
First, identify the right cloud environment:
• Public cloud services let users have access through the internet or dedicated connections.
• Private cloud keeps data within the data center and uses proprietary architecture.
• Hybrid cloud uses a mix of public and private cloud models and transfers data between the two.
• Multi-cloud lets a company use IaaS options from more than one public cloud provider.
When researching which cloud environment is right for the company and for the migration process, consider how well the data and applications will perform once migrated. In addition, determine if an application’s dependencies will complicate the migration during the process.
A few of the most used hybrid and multi-cloud environments are:
If the company is in need of a container-based PaaS cloud, consider using Cloud Foundry or Red Hat OpenShift.
Applications and data that live in the cloud needs a different management approach than when using local servers. The enterprise will need employees who understand how cloud migration works to oversee the processes and storage of data and applications on the cloud. By ensuring all employees are professionally trained for the cloud migration process can eliminate unwanted surplus charges later on.
A few of the big IaaS providers, AWS, Microsoft, and Google offer free trial tiers for a limited number of months and often with a stipend during the trial period. A few other cloud providers use the pay-per-usage model by only paying for the data that is used within a specific time like month-to-month. This can help the company estimate a more reasonable budget and how much cloud data they will need during the migration and after.
Cloud Migration Strategy Checklist
1. Asses the on-premises infrastructure and application fleet.
2. Map application, network and data dependencies and topology
3. Select applications most suited for cloud migration, and asses cloud service options to map selected applications to the optimal choice of IaaS, PaaS or SaaS.
4. Develop a migration plan and process flow to account for important details, such as data replication, account logins and connections to dependent apps.
5. Create the appropriate cloud hosting environment for IaaS or PaaS legacy migration.
6. Replicate application images and dependencies.
7. Stage and test applications in a pilot environment. Migrate beta users o simulate real-world conditions.
8. Check the final pilot environment for security and regulatory compliance before cutting over. Finally harden security, and optimize performance as necessary.
Cloud Migration Process
The process of cloud migration varies based on several factors. A few of the factors depend on the evaluation of performance and security requirements, selection of cloud provider, cost estimation, and necessary reorganization.
Be prepared to resolve some of the common obstacles during a cloud migration, including:
• Interoperability
• Data and application portability
• Data integrity and security
• Business continuity
A migration could degrade the performance of the data and applications, and lead to higher IT costs, outweighing the benefits of cloud migration.
The company will need to ensure to migrate only the high important or specific geographic data and applications to the cloud as local applications and data may not see an increase in performance and may not have the support the cloud will provide. Moreover, migrating over low importance data and applications can be monetarily unwise causing a company’s budget to exceed more than necessary.
Why Migrate to the Cloud?
Thinking about taking advantage of cloud services is a step towards growth within a company’s journey to modernize their business. In the end, the decision to use a cloud service and begin the process of cloud migration should not be done in haste. Here are a few of things to consider to help you make the right decision:
• Cloud migration brings flexibility, however, it also comes with some drawbacks. If data needs more resources to maintain performance when using a cloud provider, costs may escalate.
• Public cloud is scalable through a pay-per-usage model. Private cloud has increased control and security. Hybrid cloud uses both features of a public and private cloud but will have a decrease in performance and connectivity.
• Legacy applications or data that requires low latency or higher security and control needs to stay on the company’s on-premises infrastructure or migrate to a private cloud.
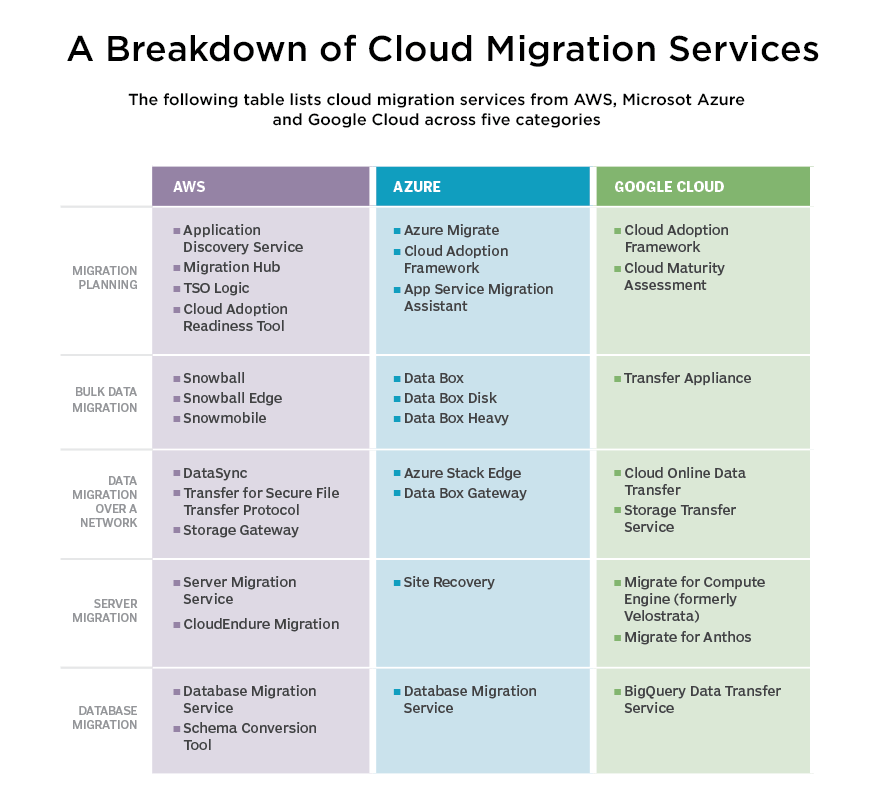
Choosing a cloud provider to migrate applications and data needs to be considered with all positive and negative aspects for the company to move forward with cloud migration. The top three cloud providers are Google, AWS, and Microsoft. All three offer comparable services allowing data to be run in the cloud with the help of additional tools to move applications, as well.
By assessing the company’s specific needs of availability, support, security and compliance, and pricing will ensure a positive outcome in the cloud migration journey.
Contact the team at VUSE to discuss which approach may be beneficial to your company and your company’s needs for cloud migration.